Introduction
Avascular necrosis (AVN) is a serious bone condition that mainly affects the hip joint but can also involve other joints like the knee or shoulder. This disease results from a loss of blood supply to the bone, causing the bone tissue to die and collapse eventually. In India, AVN treatment has seen significant advances, especially with minimally invasive regenerative therapies that aim to restore the health of the bone without major surgeries. In this article, we fully decode AVN treatment with a focus on what patients in India need to know.
What is AVN?
Avascular necrosis, also called osteonecrosis, occurs when blood flow to the bone is disrupted. Without a proper blood supply, the bone cells die, leading to pain, weakness, and collapse of the affected bone.
The hip joint, especially the femoral head, is the most common site of AVN in India and worldwide. Early symptoms often include hip pain and stiffness, which progressively worsen over time.
In India, AVN happens when the blood supply to the bone gets blocked or reduced. This can be caused by injuries to the joint or bone, like a fall or accident, which damage blood vessels. Long-term use of steroid medicines, often given for conditions like asthma or arthritis, also raises the risk. Other causes include heavy drinking, blood problems like sickle cell disease, and diseases that affect blood flow.
Sometimes, the exact cause is not known, but factors like genetics, medicine use, and certain illnesses all add to the risk. Early detection is crucial to prevent the disease from advancing to a stage where a total hip replacement becomes necessary.
Causes of AVN
Avascular necrosis happens when the blood flow to a bone is blocked or reduced, causing the bone tissue to die. In India, several common factors cause this condition.
- One main cause is injury to a bone or joint, such as fractures or dislocations during accidents, which damage the small blood vessels supplying the bone. Another major cause is the long-term or high-dose use of steroid medicines, often prescribed for conditions like asthma, arthritis, or lupus. These steroids affect blood flow and increase the risk of AVN.
- Heavy alcohol drinking also contributes by causing fatty deposits to clog blood vessels. Blood disorders such as sickle cell disease are common in India and disrupt blood circulation, increasing the chance of AVN. Certain diseases like lupus, diabetes, and infections such as HIV also affect blood supply to bones.
- In rare cases, treatments like chemotherapy or radiation may damage blood vessels. Sometimes, the cause is unknown, but likely involves a mix of genetic and environmental factors.
- Lifestyle habits like smoking and excessive alcohol use increase risk. Poverty and limited healthcare access can worsen outcomes by delaying early diagnosis and treatment.
Early detection and control of these causes are critical to prevent the progression of AVN and avoid severe joint damage.
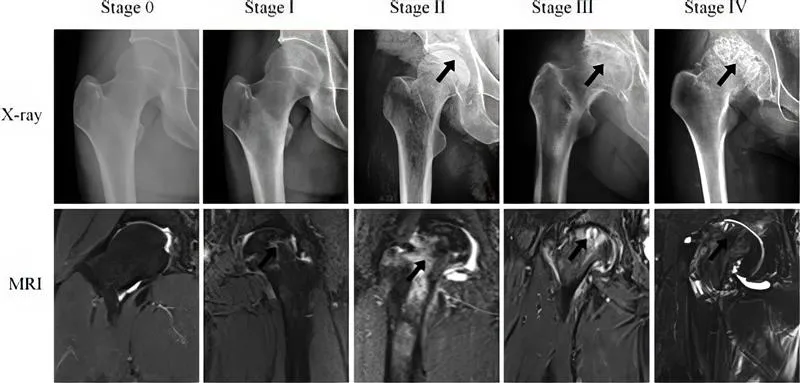
Stage 1 and 2 (Early Stage)
In the early stages of AVN, bone damage has begun, but there is no collapse of the bone structure yet. At this point, X-rays often appear normal, making diagnosis difficult without advanced imaging like MRI scans, which reveal early changes in the bone tissue.
The focus of treatment during stages 1 and 2 is to halt disease progression and preserve the joint’s natural structure.
Minimally invasive options, including regenerative treatments like SVF stem cell therapy, are most effective here. Such therapies encourage new blood vessel formation and stimulate bone repair before significant damage occurs.
Patients in these stages may experience mild to moderate pain, especially after physical activity, and occasional stiffness around the joint. Rest, restricted weight bearing, and physiotherapy complement medical treatments to support recovery.
Stage 3 (Intermediate Stage)
Stage 3 marks the beginning of structural change, as the affected bone starts to collapse. This stage often shows a characteristic “crescent sign” on X-rays or MRI, indicating a subchondral fracture under the joint surface.
Although the joint surface may still be intact, the weakening bone can cause increased pain and reduced mobility. The priority of treatment at this stage is to manage symptoms effectively while trying to delay or avoid the need for major surgical procedures.
In India, minimally invasive regenerative therapies remain valuable at this stage for carefully selected patients. These treatments improve bone quality and may slow progression. Supportive measures, such as pain management and physiotherapy, also play a critical role.
Stage 4 and Beyond
By stage 4, the bone collapse has become severe, leading to joint surface destruction and arthritis. This results in constant pain, stiffness, and significant loss of joint function. At this advanced level, conventional treatment often involves total joint replacement surgery.
However, for patients who are not candidates for surgery or prefer to avoid it, advanced regenerative therapies like SVF treatment may still offer benefits in symptom relief and functional improvement, though they may not completely reverse joint damage.
- It is important to emphasise that early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing progression to this advanced stage. In India, increasing awareness and access to MRI scans can aid in timely detection and better outcomes.
Preventive Measures
While it is not always possible to prevent AVN entirely, certain steps help reduce the risk or slow its worsening. Avoiding injuries by taking care during physical activities is important. If steroids are needed for medical conditions, use them only as prescribed and under medical supervision. Limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking support better blood flow to the bones. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints. For those with blood disorders or chronic illnesses, regular health check-ups and early treatment may lower AVN risk. Taking these precautions helps protect bone health and improves overall joint longevity.

Minimally Invasive Regenerative Treatment: The Preferred Approach
At our centre, we specialise exclusively in minimally invasive regenerative treatment for AVN using autologous stem cells derived from SVF (stromal vascular fraction). This approach avoids major surgery like total hip replacement, focusing instead on stimulating the body’s natural bone healing processes.
What Is SVF Treatment?
SVF treatment involves isolating a potent fraction of stem cells and growth factors from the patient’s own fat tissue. These cells are then injected precisely into the affected bone area under image guidance. The regenerative cells promote new bone growth, repair damaged tissue, and restore blood supply.
Why Choose SVF Treatment?
- It is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure with no large incisions.
- The treatment targets the root cause of AVN by regenerating healthy bone.
- It prevents or delays the progression of bone collapse.
- Patients experience significant pain relief and improved joint function.
- There is minimal downtime, allowing a faster return to daily activities.
- It avoids the risks and complications linked to major joint replacement surgery.
Additional Medical Treatments Available in India
While regenerative therapy is a breakthrough, other medical treatments support AVN management in India:
- Bisphosphonates: Medicines that slow bone loss and help prevent collapse. Long-term use has shown success in halting progression in early AVN stages.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs ease symptoms but do not treat the underlying cause.
- Physiotherapy and Lifestyle Changes: Exercises prescribed by specialists improve joint mobility and muscle strength while avoiding activities that stress the hip, such as running or jumping.
It is important for patients to avoid unscientific treatments or delay medical advice, as early intervention is essential to a better outcome.
Recovery and Lifestyle After AVN Treatment
Recovery time depends on the treatment type and disease stage. After regenerative therapy, patients usually return to normal activities within a few weeks, under guidance.
Cultural practices like sitting cross-legged or squatting are important aspects of life in India. Orthopedic surgeons and physiotherapists tailor rehabilitation to enable a safe return to these activities whenever possible.
Patients should maintain a healthy weight, avoid smoking and alcohol, and follow medical advice strictly to support long-term joint health.
Why Early Detection and Treatment Matter in India
In India, late diagnosis of AVN is common due to a lack of awareness and limited access to advanced imaging. Early symptoms such as mild hip pain should prompt a timely medical evaluation with specialists.
Early diagnostic tools like MRI and appropriate referrals enable treatment before irreversible damage occurs. Early intervention with minimally invasive regenerative therapy significantly reduces the need for joint replacements later.
Patient Guidance After Diagnosis
Once diagnosed with AVN, it is vital to follow your medical team’s advice closely. Avoid putting too much weight on the affected joint until your doctor says otherwise. Use assistive devices like crutches if recommended. Engage in gentle physiotherapy exercises that enhance joint movement and strengthen muscles without straining the joint. Follow-up appointments with imaging tests are essential to monitor progress. Maintain a balanced diet and adopt a lifestyle that supports bone health. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake as both harm blood circulation. Early treatment and disciplined lifestyle changes improve outcomes and preserve joint function over time.

Key Takeaway
The key takeaway from the article is that avascular necrosis (AVN) is a progressive bone disease caused by loss of blood supply, primarily affecting the hip joint. Early diagnosis and minimally invasive regenerative treatments like SVF therapy are crucial to halt progression and preserve the joint. These treatments reduce pain and improve function without the need for major surgery. Timely medical intervention enables better recovery and helps patients maintain their lifestyle with improved mobility and comfort.
FAQ's
Q1: What causes AVN in Indian patients?
Common causes include prolonged steroid use, trauma, sickle cell disease, excessive alcohol, and other medical conditions disrupting blood supply to the bone.
Q2: Is AVN curable without surgery?
Yes, in early stages, AVN is treatable with minimally invasive regenerative therapies like SVF stem cell injections that stimulate bone healing.
Q3: How long does recovery take after AVN regenerative treatment?
Most patients resume normal activities within weeks, with full benefits seen over a few months under medical supervision.
Q4: Can I continue my cultural practices after AVN treatment?
Yes, Indian orthopedic centres focus on rehabilitation that preserves the ability to sit cross-legged, squat, and perform other culturally significant activities.