Introduction
Avascular Necrosis (AVN) is a condition where bone tissue dies due to an inadequate blood supply. It leads to the weakening of the bone and may cause the affected joint to collapse.
AVN typically affects
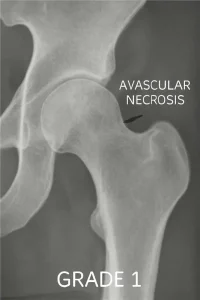
It can occur in the hips, but it can also occur in other joints like the knees, shoulders, and ankles. In its early stages, Grade 1 damage is not visible on X-rays but still requires care.
India’s expanding healthcare infrastructure offers various treatment options for AVN. Recognising symptoms, diagnosing the cause, and considering possible therapies is crucial in order to achieve maximum results; this article will focus on Grade 1 AVN treatment methods available in India.
What is AVN Grade 1?
AVN is classified into different grades, with Grade 1 being the earliest stage. At this point, the bone may show signs of reduced blood flow, but no significant structural damage is visible on an X-ray. Bones start to weaken due to an insufficient blood supply, yet they have not yet collapsed completely. Initial symptoms may be mild; patients may only become aware of their condition once it worsens further.
Symptoms:
- Mild pain in the joint, especially after activity.
- Some stiffness in the joint.
- Discomfort during movements that involve the affected joint.
If diagnosed early, AVN Grade 1 can be managed effectively with conservative treatments, and progression to higher grades can be prevented.
Causes of AVN
AVN occurs when blood flow to the bone is reduced or blocked. There are several potential causes of AVN, including:
- Trauma: Fractures or dislocations can damage blood vessels, cutting off blood supply to bones and decreasing their ability to regenerate.
- Corticosteroid Use: Prolonged use of corticosteroids has the potential to damage blood vessels and result in Avascular Necrosis of the Femur (AVN).
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol increases the risk of Avascular Necrosis by altering the blood supply to the bone.
- Certain medical conditions, such as Lupus, diabetes, and sickle cell anemia, increase your risk for AVN.
- Blood Clots: Conditions that cause blood clots can limit blood flow to bones, leading to AVN.
Understanding the cause of AVN is crucial in determining the treatment plan. In many cases, the exact cause may not be known.
How is AVN Grade 1 Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of AVN is typically done through imaging tests. However, in Grade 1 AVN cases, changes to bone are often undetectable on standard X-rays; thus, requiring doctors to use more sophisticated methods like MRI or CT scans in order to detect its early stages.
Common diagnostic methods include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This is the most sensitive test for detecting early AVN. MRI can show changes in the bone’s blood supply and detect damage before it is visible on X-rays.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A CT scan can help in evaluating the extent of bone damage and is sometimes used if an MRI is not available.
- X-rays: While X-rays may not show AVN in its early stages, they are useful for tracking the disease’s progression in later stages.
Once AVN is diagnosed, doctors assess the severity of the condition using a grading system, ranging from Grade 1 (early stage) to Grade 4 (advanced stage). Early diagnosis of Grade 1 AVN increases the chances of preventing further damage.
Treatment Options for AVN Grade 1
In the early stages of AVN, especially Grade 1, the condition can typically be treated with minimal invasive surgery. At this stage, treatment should aim to stop further progression, alleviate symptoms and protect bone integrity from collapse. There are various conservative solutions available including lifestyle modifications, medications and physical therapy; all can potentially provide positive results.
- Rest and Activity Modification
The first step in managing AVN Grade 1 is to reduce stress on the affected joint. It may involve:
- Resting affected joints: By limiting use and avoiding activities that put strain on the joint, you can ease symptoms.
- Use assistive devices: Crutches and walking aids can be an important tool in relieving pain, reducing damage, or preventing further injury.
Under certain conditions, bracing or casting may be used to immobilise a joint and ease symptoms depending on its severity.
- Medications
While medications cannot cure AVN, they are used to manage symptoms. The main goals are pain relief and inflammation reduction. Common medications include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications are used to reduce pain and swelling.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications may be recommended to alleviate discomfort.
If the pain cannot be effectively controlled, additional medications may be required.
- Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays an important role in managing AVN. A physiotherapist will work with the patient to:
- Improve joint flexibility.
- Strengthen muscles around the joint to reduce pressure on the bone.
- A guide on how to perform exercises that do not strain the affected joint.
Gentle exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and low-impact activities that improve the function of the joint without overloading it.
- Core Decompression Surgery
Core decompression may be recommended if conservative treatment does not work or AVN has progressed to a more serious stage.
This procedure involves removing a small portion of the bone to reduce pressure and improve blood flow to the affected area.
In India, core decompression is commonly performed at reputable hospitals and orthopaedic centres. While this surgery is most effective in early-stage AVN, it may also be used in later stages if the bone has not yet collapsed completely.
- Bone Grafting
Bone grafting may be necessary in certain instances to replace damaged tissues in joints that have suffered joint damage, involving transplanting bone tissue from one part of your body to the affected joint or using donated bone to do this.
Bone grafting is sometimes necessary to restore joint function and promote new bone growth when core decompression does not work or when the bone has collapsed. This procedure is designed to support existing joints while simultaneously promoting new bone growth.
- Stem Cell Therapy
Emerging research suggests that stem cell therapy may be a promising treatment for AVN. Stem cells have the potential to promote the regeneration of damaged bone tissue and improve blood flow to the affected area. While still in experimental stages, stem cell therapy is being explored in India at specialized medical centres and may become a more widely used treatment in the future.
- Total Joint Replacement
In advanced cases of AVN, when the bone has collapsed, a total joint replacement (TJR) may be the only option. It involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial one. Joint replacement surgery is commonly performed in India, where it is considered a highly successful treatment for advanced AVN, particularly in the hip and knee joints.
Preventing the Progression of AVN
Early intervention is key for preventing AVC from progressing to higher grades, where surgical options become increasingly invasive. The following steps can help in preventing the condition from worsening:
- Follow the treatment plan: Adhering to prescribed medications and physical therapy can slow the progression of AVN.
- Avoid high-impact activities: High-impact exercises, like running or jumping, should be avoided as they put strain on the affected joint.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have conditions such as diabetes or lupus, it is important to manage them effectively to reduce the risk of AVN.
Limit alcohol consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can help prevent further damage to the blood vessels and bone tissue.
Managing AVN with Yoga
In India, yoga is widely practiced for its numerous health benefits. For people with AVN, certain yoga poses can help manage symptoms and improve joint mobility. However, it is essential to work with a qualified yoga instructor who understands the needs of individuals with joint issues.
Useful yoga poses for AVN patients include:
- Supta Padangusthasana: This pose helps stretch the hamstrings and relieve tension in the hips.
- Setu Bandhasana: A gentle backbend that strengthens the hips and alleviates lower back pain.
- Baddha Konasana: This seated pose improves flexibility in the hips and enhances blood flow to the affected area.
Yoga should be practiced with caution, ensuring that movements do not exacerbate symptoms.
Conclusion
If diagnosed early enough, AVN Grade 1 can be managed successfully with treatment including rest, medication, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. Lifestyle modifications like limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding high-impact activities also play a vital role in mitigating further damage to the nervous system.
Healthcare providers in India provide various treatments for AVN, from conservative management and surgical solutions to more invasive options. It is advised that patients consult an experienced orthopaedic specialist in order to decide the most effective path forward based on the severity of their condition.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for AVN, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and maintain an active, pain-free lifestyle.